The battery is located in the underbody of the
The waterproof housing is a sandwich construction consisting of a cover at the top and a bulkhead plate at the bottom. The truss-design battery frame with multiple subdivisions is mounted in between. The cooling elements are glued on underneath the bulkhead plate. The battery housing is secured by means of a steel protective plate. For the battery frame, the developers opted for a lightweight aluminium design. On the one hand, this provides a lot of installation space for the cell modules – and consequently a high battery capacity. On the other hand, this has made it possible for the vehicle weight to be kept low. Modern joining techniques are used, such as MIG welding (Metal welding with Inert Gases) on the battery frame, laser welding on the bulkhead and protection plates, and heat-conducting adhesive on the line system under the battery (see below).
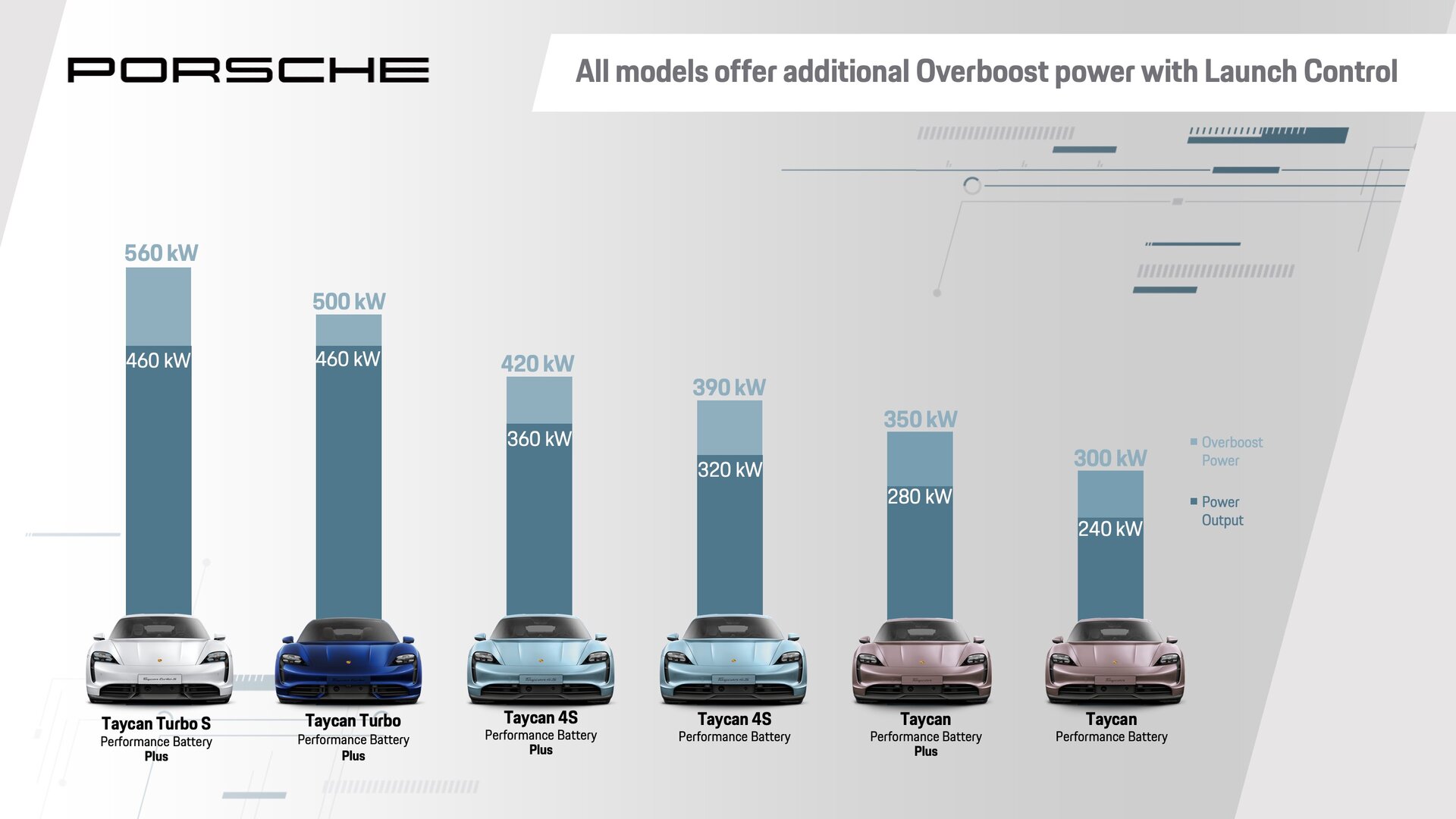
The two-deck Performance Battery Plus (standard in the
The cells themselves are pouch cells. In this cell type, the electrode stack is not enclosed by a rigid housing, but by a flexible composite foil. This allows optimal use to be made of the rectangular space available for the battery as well as a reduction in weight.
The modules each have an internal control unit for monitoring voltage and temperature and are connected to each other via busbars.
800-volt system voltage: less weight, faster charging
With the Performance Battery Plus, the
Heat pump permits intelligent functions
The battery is integrated into the vehicle’s cooling circuit via a line system and a coolant pump. It can be cooled or heated so that it always operates in an ideal temperature window. The cooling elements have been placed outside the actual battery box and are glued to its underside so as to allow heat transfer. The fundamental development aim was to dissipate as little heat as possible into the environment and thus be as energy-efficient as possible in winter.
The battery can also store the waste heat from the liquid-cooled high-voltage components. As a result, it serves as a thermal storage device or buffer, which permits intelligent functions, such as battery conditioning, to ensure driving performance: the target temperature of the battery is determined on the basis of the battery charge and the selected driving programme. This ensures a sporty driving performance and allows Launch Control to be used.
Depending on the outside temperature, the battery is preconditioned to a certain temperature level when the vehicle is connected to the mains for charging. The interior temperature can be preconditioned independently of the mains.
The vehicle also predicts the electrical power consumption of the air-conditioning system and the conditioning of the components based on the outside temperature, humidity and sunlight, as well as the currently selected driving mode and the respective setting of the automatic climate control system. The current range is calculated using these figures. In a parallel process, the optional PIRM (




